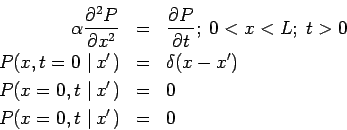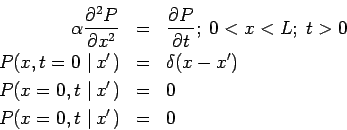

Next: PROPERTIES OF THE GF
Up: What is Green's Function
Previous: HEAT EQUATION EXAMPLE
There is a second physical interpretation of the GF for transient
problems, as follows:
the GF may also be considered as the temperature response to a
concentrated initial condition. Consider the following
boundary value problem:
The above equations are nearly identical to the equations defining G,
if the time at
which the heat source is released has been set to 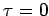 . Barton (1989)
calls function
. Barton (1989)
calls function
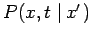 the propagator; it's
relation to the GF is given explicitly by
the propagator; it's
relation to the GF is given explicitly by
where 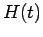 is the Heaviside unit-step function. Several GF in this
Library have been found with this view point.
is the Heaviside unit-step function. Several GF in this
Library have been found with this view point.
2004-01-21