

Next: Boundary Condition Designation.
Up: GF Numbering System.
Previous: GF Numbering System.
The GF Library includes three coordinate systems: rectangular, cylindrical,
and spherical. The numbering system has letters to denote coordinates in
each coordinate system, and one letter is needed to indicate each coordinate
present. Thus, a one-dimensional body designation contains one letter; a 2-D
body designation contains two letters, and, a 3-D body designation contains
three letters.
Rectangular coordinate system (x, y, z).
Symbol X is used to
denote the x-coordinate, Y denotes the y-coordinate, and Z denotes
the z-coordinate. Example: a 1-D plate with type 2 boundaries is
designated X22.
Cylindrical coordinate system
(r,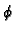 , x).
Symbol R is used to
denote the r-coordinate, symbol
, x).
Symbol R is used to
denote the r-coordinate, symbol 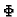 denotes angle
denotes angle 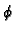 (
0 <
(
0 < 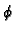 < 2
< 2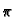 ), and symbol X denotes the axial x-coordinate. Example: 1-D
radial heat transfer in a hollow cylindrical shell with both surfaces
convectively heated is designated R33.
), and symbol X denotes the axial x-coordinate. Example: 1-D
radial heat transfer in a hollow cylindrical shell with both surfaces
convectively heated is designated R33.
Spherical (polar) coordinate system
(r,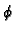 ,
,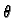 ).
Symbol RS is used to denote the spherical r-coordinate, symbol
).
Symbol RS is used to denote the spherical r-coordinate, symbol 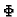 denotes
azimuthal angle
denotes
azimuthal angle 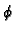 (
0 <
(
0 < 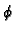 < 2
< 2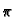 ), and symbol
), and symbol 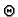 denotes the
polar angle
denotes the
polar angle 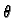 (
0 <
(
0 < 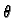 <
< 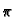 ). Example: 1-D radial heat
transfer in a hollow sphere with type 1 boundary conditions is designated RS11.
). Example: 1-D radial heat
transfer in a hollow sphere with type 1 boundary conditions is designated RS11.


Next: Boundary Condition Designation.
Up: GF Numbering System.
Previous: GF Numbering System.
Kevin D. Cole
2003-07-21